Russian Playing Card Monopoly
The Russian Playing Card Monopoly was established in March 1798 with all revenue going to support the St Petersburg Foundling Hospital. After the construction of the Foundling Hospital's own factory in 1817 (known as the Imperial Playing Card Factory), all subsequent Russian playing card production was located there until the end of the State monopoly in 1961.
Playing cards were first taxed in Russia in 1765 when a special edict was passed confirming the state’s monopoly on the production and sale of playing cards. Imported packs were subject to a duty of 10 kopeks, home produced packs to a duty of 5 kopeks. Senate decrees of 1766-1767 ordered foreign cards to be branded at the ports of St. Petersburg, Archangel, Riga and Revel. Domestic cards were branded at the Manufactory College in Moscow and the Manufactory Office in St. Petersburg. Due to general inefficiency and widespread counterfeiting that took place, the St Petersburg Office was abolished in 1779 and the right to brand cards was awarded to the Foundling Hospital (founded 1770) - a monopoly it retained until 1820 [1].



The official start of the State Card Monopoly is usually given as March 1798 when a Decree was issued by Tsar Paul I in which “the right to brand and sell cards throughout the Russian Empire is forever assigned to the Orphanage”. The decree was issued at the request of Empress Maria Fedorovna, the wife of Paul I and patron of the Orphanages.
Initially tax was paid directly to the foundling hospitals by the manufactories at the rate of 5 kopeks per pack. Very soon, due to the obvious opportunities of cheating the system, the St. Petersburg foundling hospital assumed legal responsibility for producing the individual pack seals. It was probably at this time that the symbol of the Institutions of the Empress Marie was devised: a pelican nurturing her young with the flesh from her own heart. On some of the cards, in addition to the usual motto of “For the benefit of the Imperial Foundling Hospital” was the phrase “Not sparing herself she nourishes her fledglings”.
Although the Foundling Hospital controlled the sealing of packs, abuse continued in the form of large-scale tax evasion or production of non-officially sealed packs – so much so that it was decided to place the job of revenue collecting into the hands of “tax farmers” (otkupshchiki). The Russian system of otkup was a system for collecting duties and other state revenues, under which the otkupshchiki paid the government annually a fixed sum to buy the monopoly on customs-collecting in a given area or commodity. There were tax farmers for a whole variety of commodities or activities (e.g. tobacco, the fishing industry, etc.). The amount collected over and above the state-appointed sum was retained by the otkupshchiki as his profit. Otkup for playing cards lasted for 20 years between 1799-1819.
The right to collect duties was contracted out every four years. Thus there were five otkupshchiki in this period. The amount paid for the privilege grew considerably, indicating the inexorable growth of playing card production [2].
- 1799-1803: Cheblokov & Kusovnikov - 140,000 roubles
- 1803-1807: Cheblokov, Zlobin - 150,000 roubles
- 1807-1811: Obolonskii, Fadeev - 257,000 roubles
- 1811-1815: Shakhovskoi, Petrovo-Solovovo - 350,500 roubles
- 1815-1819: Tatishchev, Volkonskii - 400,000 roubles
Eventually the Patronage Committee of the Hospital decided to take responsibility for the manufacture of playing cards rather than rely on otkup, or indirect revenue raising. The intention was to build a factory under its own administration, with the labour coming from the older children and former pupils of the foundling hospitals. It was calculated that profit could be as high as 34-39 kopeks per pack (in contrast to the 5 kopek tax).
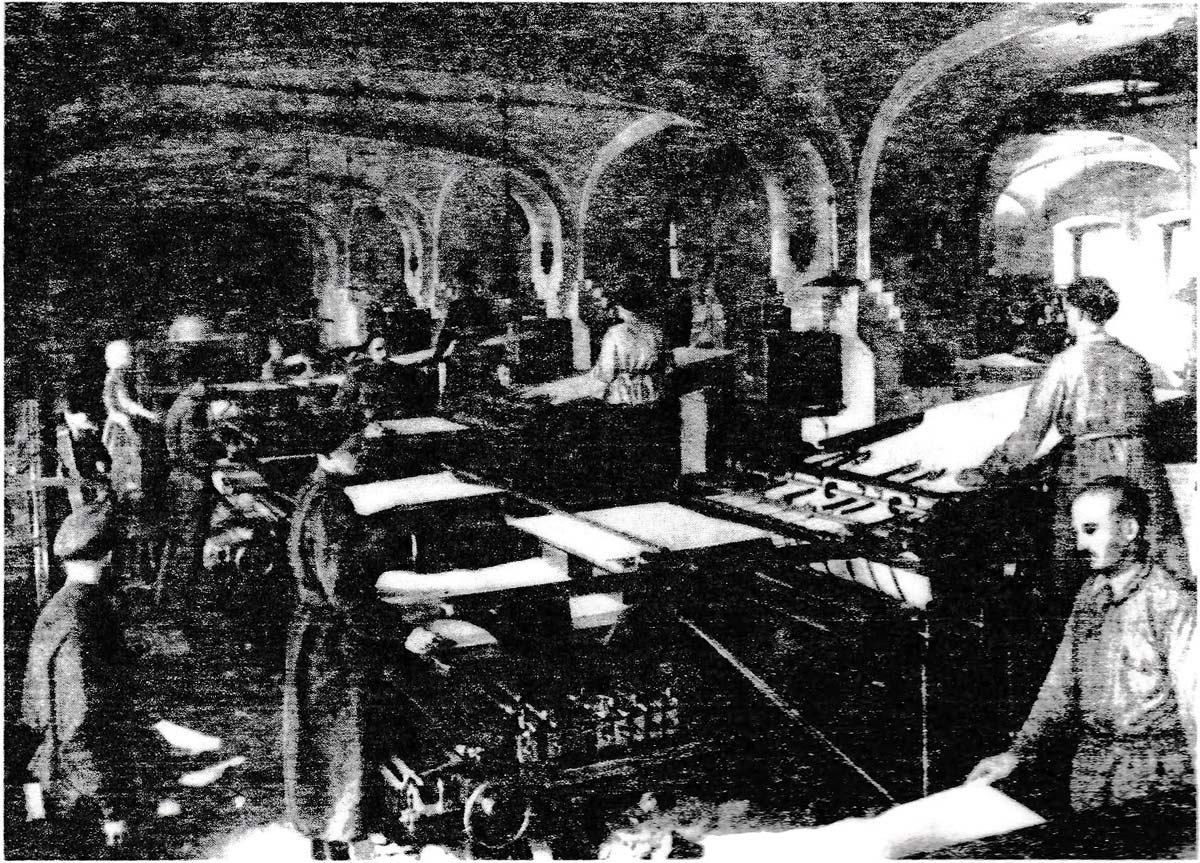

Above: workers in the printing room of the playing card factory, early 1920s. Poltora veka [3].
The site chosen for the establishment of the Imperial Playing Card Factory was in the grounds of the existing Aleksandrovskii textile mill, founded in 1798 and which had been placed in 1799 under the aegis of the foundling hospitals.
The official foundation of the Imperial Playing Card Factory is accepted as 2 October 1817 (Old calendar), 24 October (New style). The cost of its establishment was 207,000 roubles – a sum considered justified in the expectation of receiving profits of some 401,000 roubles per annum [3].
On October 12, Tsar Alexander I signed a resolution on a note by Empress Maria Feodorovna on card redemption: "I agree with the will of Your Imperial Majesty in everything." This entry decides the creation of a special Card Factory in order to "stimulate the domestic manufacture of playing cards", as well as the destruction of all card-farming that currently exists.
Production of cards began in April/May 1819 (at which time the otkup on cards was finally abolished). One of the first packs produced by the Imperial Playing Card Factory, c. 1820 was the "Russian Tarok" or "Animal Tarok"►

Above: Russian “Historical” playing cards with designs by Nikolay Karazin, 1897.

Above: Russian style playing cards first published in 1911.
Until 1860 the Imperial Playing Card Factory was located at the Aleksandrovskii Manufactory in St. Petersburg. In 1860 the Alexandrovskii textile mill collapsed unable to keep up with private and foreign competition, and owing 20,000 roubles to the playing card manufactory.
From 1860-1917 the Imperial Playing Card Factory was located at the Imperial Educational House, St. Petersburg. In 1914 the city’s name was changed to Petrograd.
In 1918-1919 and 1922-1935 it was called the State Card Factory (Goskartfabrika) in Petrograd (and Leningrad from 1924). In 1920 and 1921 the factory was closed due to Civil War in the country.
From 1935-1958 another change of name to the Second Art Lithography factory, Leningrad (2-ia Khudozhestvennaia Litografiia). Unfortunately, most of the archives were destroyed during WWII and the siege of Leningrad.
1958-1964 it was known as the Third Offset Printing Factory, Leningrad
1964-1967 the Leningrad Offset Printing Factory, No. 3
1968-2004 Leningrad Colour Printing Works (Kombinat Tsvetnoi Pechati).
In 1961, the State Card Monopoly was legally abolished.
In 2004 the Kombinat Tsvetnoi Pechati ceased to exist.
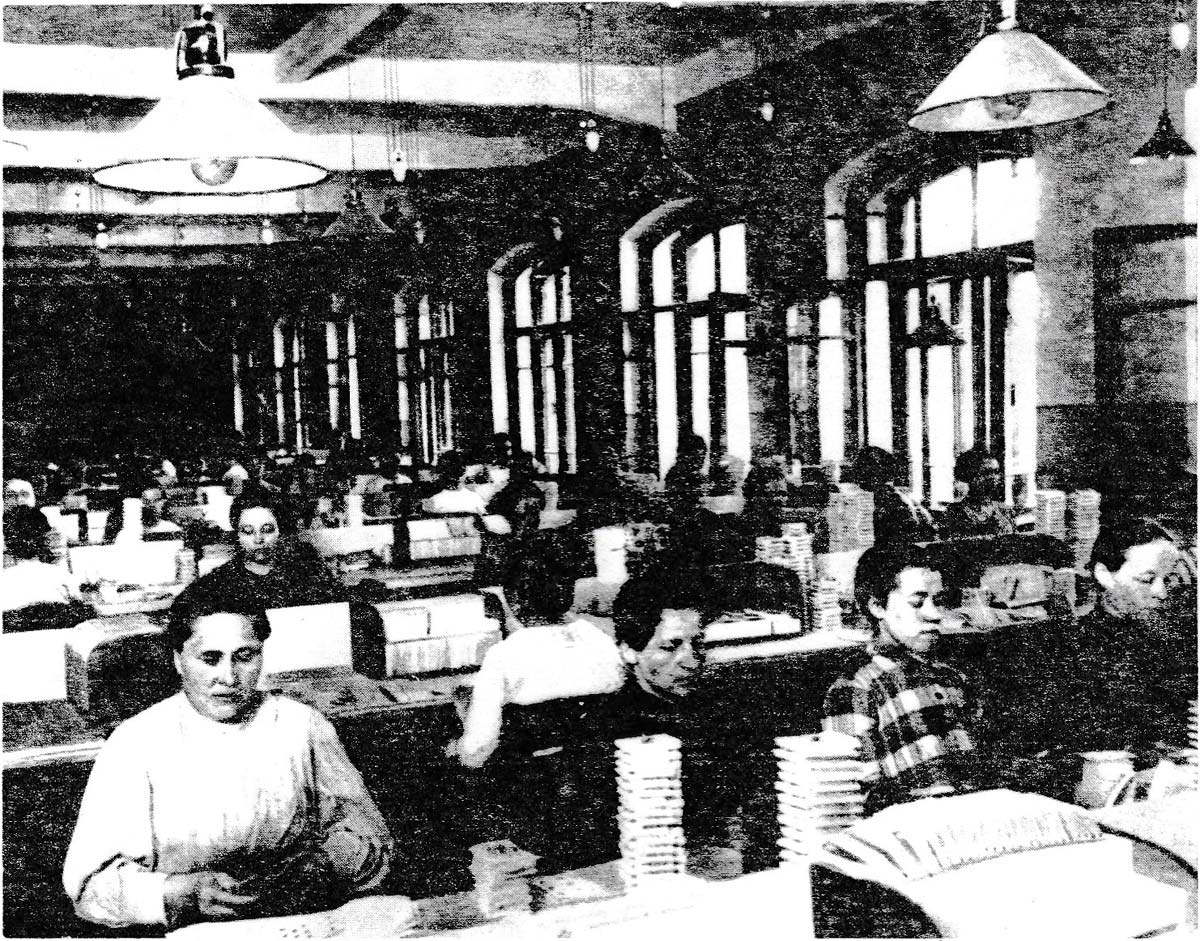

Above: workers sorting cards in the playing card factory, early 1920s. Poltora veka [3].
Identification of Playing Cards [4]
Although the right to brand cards was awarded to the Foundling Hospital in 1779, the otkup system meant that the branding of cards also began to be leased out.
From 1803-1807 the brand /stamp was placed on the two of hearts (first quality), two of diamonds (second quality) three of hearts (third quality)
From 1807-1811 the brand/ stamp was placed on the ace of hearts (first quality), the ace of diamonds (second quality), the ace of spades (third quality)
From 1815-1819 the brand / stamp was placed on the ace of spades (first quality), three of diamonds (second quality), the two of clubs (third quality)
Later on, the brand / stamp was generally placed on the ace of diamonds for expensive packs and the ace of clubs in others.
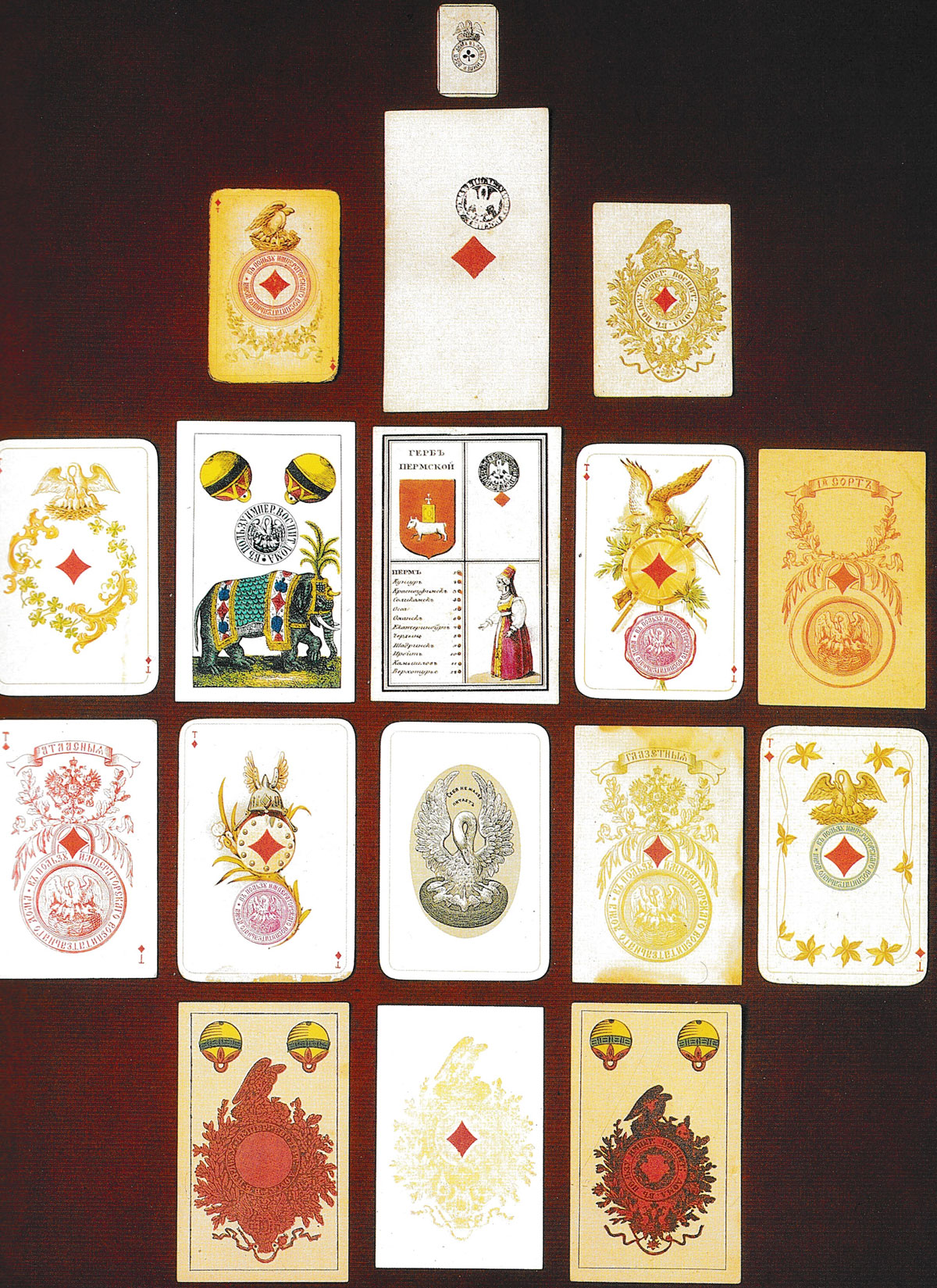

Above: tax stamps on early Russian cards. From the State Russian Museum, Play and Passion, Spb, 1999, p. 225.
FOOTNOTES and REFERENCES
1. State Russian Museum, Play and passion in Russian fine art. (St Petersburg, Palace Editions, 1999) p. 224.
2. Lesnoi, Dmitrii, Entsiklopediia igornyi dom. (Moskva, Liga Mir, 2006) p. 479.
3. Poltora veka: ocherki, dokumenty, vospominaniia, materialy [k 150-letiiu istorii Leningr. Kom-ta tsvetnoi pechati] (Leningrad, 1969).
4. State Russian Museum, Play and passion in Russian fine art. (St Petersburg, Palace Editions, 1999) p. 224.
Burnett, P.P.: “Russian playing card history: from the beginnings to 1917”, published in The Playing Card, 13 (4), May 1985, pp. 97-113 and reprinted in The Playing Card, 40 (1), Jul-Sep 2011, pp. 41-57. Download here►
By Peter Burnett
United Kingdom • Member since July 27, 2022 • Contact
I graduated in Russian and East European Studies from Birmingham University in 1969. It was as an undergraduate in Moscow in 1968 that I stumbled upon my first 3 packs of “unusual” playing cards which fired my curiosity and thence my life-long interest. I began researching and collecting cards in the early 1970s, since when I’ve acquired over 3,330 packs of non-standard cards, mainly from North America, UK and Western Europe, and of course from Russia and the former communist countries.
Following my retirement from the Bodleian Library in Dec. 2007 I took up a new role as Head of Library Development at the International Network for the Availability of Scientific Publications (INASP) to support library development in low-income countries. This work necessitated regular training visits to many sub-Saharan African countries and also further afield, to Vietnam, Nepal and Bangladesh – all of which provided rich opportunities to further expand my playing card collection.
Since 2019 I’ve been working part-time in the Bodleian Library where I’ve been cataloguing the bequest of the late Donald Welsh, founder of the English Playing Card Society.

Leave a Reply
Your Name
Just nowRelated Articles

Castle Rock Club
Castle Rock Club playing cards featuring Russian rock stars and musicians, c. 2000.

Russian Playing Card History - From the Beginnings to 1917
An in-depth review of the history of card-playing, gambling, legislation, manufacture and taxation o...

Russian Playing Cards
Playing cards were known in Muscovy as early as the last quarter of the sixteenth century.

Saint Petersburg vintage playing cards
Saint Petersburg vintage photography playing cards.

Madam Luck
“Madam Luck” playing cards designed by B. Adziev, 1998.

Lubok playing cards
Lubok playing cards designed by Victor M. Sveshnikov. Russia, 1984.

Soviet propaganda posters
Propaganda posters of the Soviet Union.

Russian Federation
Russian Federation pack featuring leading political figures of the time, c.2000.
![Komandirskie [Commanders] Komandirskie [Commanders]](/core/cache-wopc-thumbs/var/www/wopc/production/www/images/countries/russia/komandirskie-0.45cc333d.jpg)
Komandirskie [Commanders]
‘Komandirskie’ military-themed playing cards from Russia, 1997.

Peterhof souvenir playing cards
Peterhof souvenir playing cards (Petergof suvenirnye igral’nye karty) published by Mednyi Vsadnik (B...

Pushkin
Pack designed by M. Rydaeva celebrating the 200th anniversary of Alexander Pushkin’s birth.

Dolls Gallery
Dolls Gallery / Galereia kukol : karty igral’nye / published by Varvara Skripkina, 2003.

Treasures of the Russian Museum
Treasures of the Russian Museum / Russkii Muzei : suvenirnye igral’nye karty.

Russian Cities Coats-of-Arms
Rossiia / Municipal Coats-of-Arms of Russian Federation.

Matryoshka playing cards
The first nested doll set was carved in 1890.

Palekh and Kholui lacquer miniatures
Palekh and Kholui lacquer miniatures.

Hunting playing cards
Hunting playing cards / “Okhotnich’i karty” with illustrations by the court artist Mihály Zichy.

Russian Emperors
Russian Emperors playing cards / “Rossiiskie imperatory karty igral’nye” produced and illustrated b...

Russian Beer
Russian Beer playing cards / “Russkoe pivo karty igral’nye” produced in 2006

Rokoko
Rokoko (Rococo) reflecting the dress and culture of the first half of the 18th century.
Most Popular
Our top articles from the past 60 days


 Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here.
Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here.