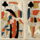Logica Memorativa
Logica Memorativa playing cards by Thomas Murner, Brussels, 1507.
Logica Memorativa playing cards by Thomas Murner, 1507










1. The face of this World is subject to the face of the heavens. 2. This locus has Gemini its basis. 3. The rider is Perseus, 'La Morte', here depicted as a femme fatale. 4. Modelled on Canis minor, the more northerly of Orion's two 'dogs' 5. Capricorn, reworking the older model of Auriga as 'Magus' 6. A very interesting adaptation of Orion's form. 7. The astronomical locus is the furthest extreme of the southern heavens. 'Strength.' 8. Here the heavens' 'fallen angel' Canopus. 9. Probably based on Canis major, whose chief star's character as Sothis, 'the piercing supporter' was well known in Europe. Semaphoros.
Influenced by Byzantium, Vittorino da Feltre's school 'La Giocosa' revived in Italy the habit of using exercise-games in elementary levels of teaching. From that model, perhaps, the Franciscan named Thomas Murner in the late fifteenth century devised his course for teaching elements of logic. He presented students (in parallel with his 16 written lectures as 'Letters' or charta), with suites of practical exercises and mnemonic diagrams to supplement and reinforce students' memory of the material. Each lecture was linked with its associated exercises and diagrams by use of a common emblem, the 16 emblems speaking to philosophical symbolism and to stages of progress through academe's 'little year.' In 1509 an outline of his astonishingly successful method was published - probably by the University of Cracovie where Murner taught ' under the chief title Logica Memorativa: 'Memorials of Logic.' The published book provides an outline of that teaching method, together with the format for students' exercise-games and copies of the mnemonic figures. Hargraves quotes an anonymous inscription, dated 1842, which suggests Murner's success was due to the 'use of a card-game to teach logic' but this is an exaggeration, for although the book's advertisement does distinguish between the new style of elementary teaching: 'chartiludum logice' and the token-using exercises: 'cum iucundo [iuc = joc] pictasmatis exercito' Murner's intention was not to teach logic by means of a card-game so much as to offer the sort of programme composed of text, exercises and demonstration figures that is now usual in modern primary education. The 16 suit-signs, incidentally, should be understood as a doubled, or complementary circuit of 8 parts, the mnemonic figures as intrinsic to Murner's approach. His 16 emblems (as listed in Hargraves) were [hawking-] bell, fish, acorn, scorpion, lobster, cap, heart, grasshopper, sun, star, bird, moon, cat, shield, crown and serpent.
Connection between the principles of card-pack construction and those of
Murner's mnemonic figures is plainly evident, but so are the differences. A
card-pack's emblems normally alluded to the quarters of time and direction,
while Murner's are keyed to his sequence of lectures. The emblems and
pictorial figures in standard packs were derived ultimately from
astronomical types, but Murner separates the allusion of his suit-signs
from the astronomically-based anthropomorphic figures. The published book
omits Murner's lectures, too, which are the heart of his programme. The
University appears to have chosen instead to promote the overall method,
providing a course outline and copies of the basic materials. Our following
comments are not upon that course, but upon the sources from which Murner
himself drew when designing these memorial figures. One should consider them
as items in a thesaurus, whose reference languages are Latin, German and
Greek.
The Figures
1. Murner's guiding principle in design for his Course, its exercises and imagery, is well embodied by the figure given for [step] 4 in the Acorns' suite. We might cite a phrase from the Centiloquium: 'The face of this World is subject to the face of the heavens.' The 'World' here is represented by the female figure, whose paired mirroirs are intended to suggest the upper and lower hemispheres, as well as the 'epitome-form' itself. Books of concentrated matter - in the form of extracts from texts or figures for reflection - were then known as florilegia, tresors, thesauri or mirroirs. This figure of the World reminds us at once of the 'epitome' represented by this curriculum, and of the condensed mnemonic figures which are at hand, while at the same time alluding to the physical pinnacle of the world, the Pole star [cynosura]. We see that the 'World's' better side is given by reflection upon the higher glass, an idea emphasised by marking that glass with the theologian's number of divine perfection '1'. The opposed and lower glass is marked by the number '11' ' equally traditional as the number for error and sin. Logic's deductive and inductive processes were similarly polarised, as were most of the discursus games derived from the style of the joc.
2. The eighth locus in the Fish suite takes the constellation of Gemini as its basis. The twin to our right is understood as having been led to err (by allusion to the Gospel narratives Mat.18:6; Rev 18:21-23) while the other maintains a 'righteousness' associated with right measures and proportion. The representation of the corrupted twin's left leg conveys Murner's knowledge of Arabic nomenclature in astronomy.
3. Stage Two in the suite of the 'lobster' shows a mounted figure holding up the emblem of the heart. The rider is Perseus, 'La Morte', here depicted as a femme fatale. In other figures derived from Perseus' moral character, the heart may become a cup, since both were significant ' in astronomical lore ' of the ultimate trophy or triumph of the Pleiades. The rider displays the poor lover's heart as that trophy and naturally suggests the endlessly popular theme for discursus 'Amor vincit omnia.' But mere earthly love is not here suggested as being greater than Death itself. The rider wears a string of pearls which ' as throughout Murner's diagrams ' informs the viewer that a figure promotes carnal or earthly knowledge over spiritual wisdom, after the way of the Fool.
4. Here we see the figure for a 'bitter' lower constellation, which southerly locus in these diagrams is invariably indicated by some form of grinding tool. The woman appears to be modelled on Canis minor, the more northerly of Orion's two 'dogs'. Traditionally considered the weeping wife of a cruel master, Canis minor is called in Arabic 'al Ghumaisa' ' the weeping, but here is shown 'crying aloud' in a different sense. In many card-sets she appears with Taurus in the guise of a horned and trident-bearing demon. Her connection with the demon-as-husband goes back to Egyptian times in the east. Murner's having her uphold the 'rule of 50 ' latin L' alludes to a monastic custom of treating the 'l-rule' as symbolic of the Egyptian [and Egyptian Jewish] traders. It implies also the Egyptian habit of orienting to the 'bent' southern Pole, rather than to the eastern or northern.
5. This female figure mounted on the goat is another example of Murner's giving female form to a constellations normally depicted as male. The construction of this whole mnemonic demonstrates Murner's practical knowledge of astronomy, and his understanding but disdain of horoscopic astrology. In addition, the reversal of gender would support a religious emphasis on the stars as inanimate and gender- neuter while at the same time facilitating the 'sic et non' style of logical debate. In most card sets, though, it is Auriga who is properly the master of measures. Most often tagged 'Magus,' Auriga was patron and guide of Crete, his goat-star, Capella being identified with Amalthea, nurturer of the infant Jove on Mt. Ida. Murner, however, transfers the entire character to the constellation of Capricorn, which astrology appointed to oversee the period of Christ's birth at the winter solstice. Murner indicates this altered reference by providing Capricorn with its identifying long horns and by setting the usual grinding implement below to indicate its southerly locus. Murner takes his division between the northerly and southerly celestial figures to be the line of the ecliptic, where the older method had taken the celestial equator. Becoming general about the mid-sixteenth century, this habit of re-working the older moralised heavens very swiftly led to a complete disintegration of the old ' indeed ancient ' memorial heavens.
6. A very interesting adaptation of Orion's form, the presence of the millstone once again suggests the erroneous teachings of the 'Fool', but also that corruption invoked most notably in the d'Este pack. Murner recognises the 'three-point' of Orion's head, and makes the rearmost point especially prominent. Cloven hoofs signify always a demonic character, and so speak to another long- established strand of thought about this constellation. Murner's evident confusion about whether or not Orion is al Ghumaisa's demonic master is understandable, especially since another of Orion's conventional characteristics was that of being 'a devilish hard task-master.' This idea is to be seen again in illustrations of the Picatrix. Murner evidently thought that to beat knowledge into the young in the older way was stupid and unnecessary, his allusion to the ostrich again referring to this idea. Job 39:13-18, speaks of the ostrich as 'hardened against her young ones ' God hath deprived her of wisdom, neither hath he imparted to her understanding.'
7. The astronomical locus for this occulted 'hell's kitchen' is found at the furthest extreme of the southern heavens where monastic tradition had an anti-cynosure in the form of woman bound to the 'hell-mouth'. Her character was considered both concupiscent and brilliant - a hair-splitting disputant. She was also supposed responsible for luring ships to their doom, and was in that sense the 'breaker of ribs.' The celestial ship held securely by her magnetic attraction was the great figure Argo Navis. In more positive versions she becomes 'St. Lawrence' upon his burning grid, or Persephone, enduring endless lonely labour in the southern underworld. 'Strength' is her most common tag in card-sets.
8. Here the heavens' 'fallen angel' Canopus, a figure half-hidden and half revealed, is shown in a way that makes clear the influence of Byzantium. Canopus is the pilot-star of the southern Argo Navis as 'arca'. In most depictions he becomes the hermit lucifer, the fallen light-bringer. Murner however has adapted for his image the form of the Byzantine Perseus, which was commonly shown as the Angel of Death seated by (or on) Christ's tomb. Correctly the southern heavens' 'tomb' is a constellation below Canopus and was indeed considered the place from which souls emerged or re-emerged. The Arabs called it the Murraba' and we now know it as Crux, the Southern Cross. It appears in most 78-card packs under the tag 'le Judgement.' From the earliest period of card-use, an ancient habit which supposed that the hidden southern stars must exactly mirror the form of the northern plainly influenced the pictorial forms. Combined with the need to arrange the astronomical types by pairings, that fixed idea contributes largely to the commonly confused and inaccurate forms on card.
9. Murner's flexibility in constellation-gender makes this figure difficult to identity without comparison with the full set. I am inclined to believe it based on Canis major, whose chief star's character as sothis, 'the piercing supporter' was well known in Europe. Despite its southerly position, the constellation was widely revered in pre-Christian Italy and France, eventually being sanctified as [St.] Guinefort. It may be, however, that Murner was thinking rather of a star just above the ecliptic, a Lyrae, whose Latin name was 'fides' and whose harp in western moralia and heraldry was often made into the form of a shield. Whether identified with Sirius, with 'Fides' or even with Aquila, the figure is intended as one of a pair, companion figures to the radiant Lord travelling his east-west road. [Guinefort comes from a root meaning to signal or flash intermittently. With regard to the eye's flashing light it came to mean 'winking'.]
Logica memorativa. Chartiludium logice sive totius dialectice memoria et novus Petri Hyspani textus emendatus, cum jucundo pictasmat (Memorable logic. Playing cards logically or dialectically memorized and the new text of Peter Hispani corrected, with delightful illustrations).

Above: page 1 of treatise by Thomas Murner (1475-1537). Source gallica.bnf.fr / Bibliothèque nationale de France • Logica memorativa►
By Simon Wintle
Spain • Member since February 01, 1996 • Contact
I am the founder of The World of Playing Cards (est. 1996), a website dedicated to the history, artistry and cultural significance of playing cards and tarot. Over the years I have researched various areas of the subject, acquired and traded collections and contributed as a committee member of the IPCS and graphics editor of The Playing-Card journal. Having lived in Chile, England, Wales, and now Spain, these experiences have shaped my work and passion for playing cards. Amongst my achievements is producing a limited-edition replica of a 17th-century English pack using woodblocks and stencils—a labour of love. Today, the World of Playing Cards is a global collaborative project, with my son Adam serving as the technical driving force behind its development. His innovative efforts have helped shape the site into the thriving hub it is today. You are warmly invited to become a contributor and share your enthusiasm.

Leave a Reply
Your Name
Just nowRelated Articles

OH Cards
A Series of Metaphoric Cards to unlock your story, conceived and designed by Ely Raman

Early German playing cards
Some early examples of popular German playing cards from the XV and XVI centuries.

Iohann Christoph Hes Tarot c.1750
Facsimile of Tarot de Marseille by Iohann Christoph Hes, Augsburg, c.1750.

Georg Kapfler
Antique deck of old Bohemian playing cards of the German type manufactured by Georg Kapfler and date...

Master of the Playing Cards
Animal suited playing cards engraved by the Master of the Playing Cards, Germany, c.1455

I. Schenck, Nuremberg
I. Schenck, Nuremberg, late XVIIIth century

Arms of English Peers
The Arms of English Peers playing cards were first published in 1686. Heraldry, or a knowledge of th...

Stuttgart pack, c.1430
The luxury, hand-painted Stuttgart Cards (Stuttgarter Kartenspiel) dated c.1430, with suits of ducks...

Klipp Klapp Karten
“Klipp Klapp Karten” printed by KZWP-Trefl (Poland) for Kindermuseum Oelde (Germany) in 2004

Hans Sebald Beham
Playing cards designed by Hans Sebald Beham (1500–1550).

Kriegs-Spiel by Peter Schencken, Amsterdam
Peter Schencken of Amsterdam copied the "Jeu de la Guerre" or "Das Kriegs-Spiel" (with German captio...

Old Bavarian pattern
Uncut sheets of playing cards of the Old Bavarian pattern by Michael Schatzberger, Passau, c.1780.

Cotta Transformation playing cards
In 1804, J.G. Cotta, a publisher and bookseller in Tübingen, Germany, produced the first set of tran...

German Saxon Pattern
The German Saxon Pattern or “Schwerdter Karte”.

William Warter
William Warter's Proverbial Cards, which carry illustrations of old English proverbs, were first pub...

Geistliche Karten
Geistliche Karten, Augsburg, 1718. Each card carries a text in Gothic typeface giving advice regardi...

German playing cards
Card-playing rapidly became popular in medieval Bavaria and German printers were quick to supply the...

Robert Morden’s Playing Cards
The 52 Counties of England and Wales described as a pack of cards first published in London in 1676....

Peter Flötner, c.1545
Seven cards from a satirical pack produced by Peter Flötner of Nuremberg, c.1545. The suit symbols a...

Playing cards in the Upper Rhine region
Documentary evidence suggests that card playing established itself in Italy in 1376, and then spread...
Most Popular
Our top articles from the past 60 days


 Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here.
Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here. Your comment here.